Structure of Timber :
1)Pith : Inner most part having soft tissues near about the center of log of a timber.
2) Heart Wood : Inner Part of Log of a tree surrounding the pith is called Heart.
3) Sap Wood : Outer Part of log of a tree surrounding heard wood & upto the bark which contains living cells Is called Sapwood.
4) Cambium Layer : Layer of liquid material deposited below the bark & outside the sap wood in the log called Cambium Layer.
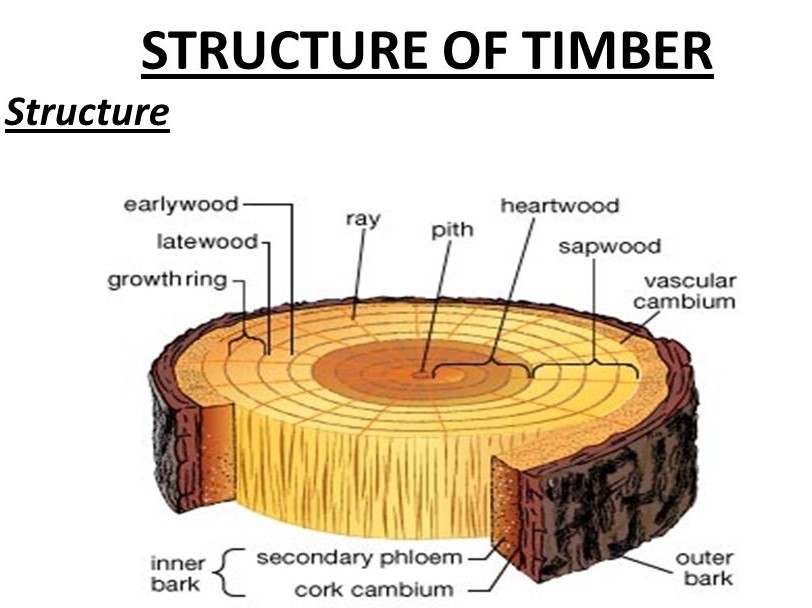
5) Inner Bark or Bast : The inner skin surrounding The Cambium Layer. This skin feed & covers the Cambium Layer.
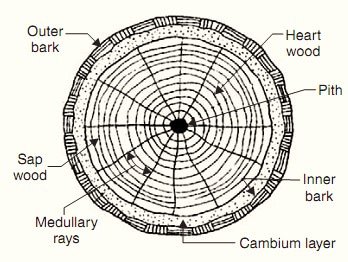
6) Outer bark : The covering outside the log of a tree.
7) Annual Ring : Concentric innumerable rings in the log of a timber,Indicating its growth are called Annual Rings.
8) Medullary Rays : Horizontal thin fibrous tissues which extended radially from the cambium layer towards the core or from the pith towards the bark.
Types / Sawing of Timber :

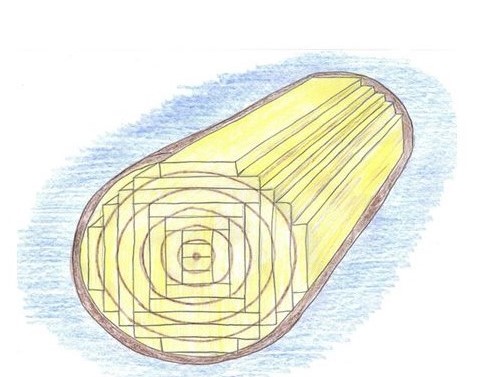
- Ordinary or Slab Sawing : Most economical method As the wastage of timer & cost of sawing minimum.Cuts are made into the log of wood according to the required thickness, not necessarily tangential to the annual rings.
- Tangential Sawing : The board & planks are sawn out of wood tangentially to the annual rings. Economical due to less wastage &involves less Labor do not suit for heavy works as for flooring.
- Quarter Sawing : Log cut into four quarters. These quarters have their flat faces essentially radial.Cuttings the annual rings at angles not less than 45Degree. It requires more labour & involve more Wastage.
- Radial or Rift Sawing : Log cut out of quarter logs Parallel to the medullary rays & perpendicular to the annual rings. Uneconomical method. It produces timer with end grains which are sometimes known as “Silver Grains” by sawing parallel to the medullary rays.Used for High Class decoration & joinery work.
- Combination Sawing : Log is converted by the Combination of two or three methods.Advantages of Ordinary & Radial Sawing.
Common Markets Forms & Sizes of Timber :
A) Log : Stem or trunk of a tree which is felled.

B) Baulk : A piece of sawn timber, cross sectional Dimension of 50mm in one direction & 200mm in other.
C) Bole : The main stem of a tree
D) Bolt : A Short log 1.25m or less in length.
E) Billet : Short length of a thin stem or branch wood.
F) Batten : Piece of sawn timber, the cross sectional dimension of which dn’t exceed 50mm.

G) Plank : Thickness not exceeding 50mm & width exceeding 50mm.
h) Board : A thin plank under 50mm thick & 100mm More Width.
I) Cant : A thick piece of timber with or without squared edges.
J) Deal : A sawn piece of wood which is 50-100mm thick & 200-250mm wide.
K) Deal Wood : Light timber used for packing cases,crates.
L) Hewn timber : Timber converted to size by an axe and the end.

M) Pole : A long, soild, straight trunk of a tree 100 To 300mm in dia.at breast height & gradually to the top, Of a diameter of 100mm or more.
N) Post : Timber member used in upright position in Building fencing or structural work is called a post.

O) Scantling : Sawn Piece , dimensions of which Exceed 50mm in both the direction bt dn’t exceed 200mm In length.
P) Slat : Wood about 185mm x 65mmx 6mm in size.
Q) Sleeper : Transverse supports under rails in a Railway track. 250mmx125mm or 200x115mm.
R) Strip : under50mm thick & less than 100mm wide.











